Overview
 Morton’s Neuroma is a common problem in runners, and there are a number of simple fixes you can try before resorting more drastic solutions like sclerosing or surgery. A Morton’s Neuroma normally causes a burning pain in the forefoot, just behind the 3rd and 4th toes (sometimes behind the 2nd and 3rd toes). The pain often radiates towards the toes, and sometimes there is numbness rather than pain. The underlying cause is inflammation of the nerve between the bones of the forefoot, often triggered by narrow or tight shoes. I have had good results with the simple fixes described below, and I have had reports of other runners with similar success.
Morton’s Neuroma is a common problem in runners, and there are a number of simple fixes you can try before resorting more drastic solutions like sclerosing or surgery. A Morton’s Neuroma normally causes a burning pain in the forefoot, just behind the 3rd and 4th toes (sometimes behind the 2nd and 3rd toes). The pain often radiates towards the toes, and sometimes there is numbness rather than pain. The underlying cause is inflammation of the nerve between the bones of the forefoot, often triggered by narrow or tight shoes. I have had good results with the simple fixes described below, and I have had reports of other runners with similar success.
Causes
Morton’s neuroma may be the result of irritation, pressure or injury. In some cases its cause is unknown. In the majority of cases only one nerve is affected. Having both feet affected is extremely rare. A high percentage of patients with Morton’s neuroma are women who wear high-heeled or narrow shoes. Patients with Morton’s neuroma may need to change their footwear, take painkillers or steroid injections, while others may require surgery to either remove the affected nerve or release the pressure on it.
Symptoms
If you have a Morton?s neuroma, you may have one or more of these symptoms where the nerve damage is occurring, Tingling, burning, or numbness, pain, a feeling that something is inside the ball of the foot or a feeling that there?s something in the shoe or a sock is bunched up. The progression of a Morton?s neuroma often follows the following pattern. The symptoms begin gradually. At first they occur only occasionally, when wearing narrow-toed shoes or performing certain aggravating activities. The symptoms may go away temporarily by removing the shoe, massaging the foot, or by avoiding aggravating shoes or activities. Over time the symptoms progressively worsen and may persist for several days or weeks. The symptoms become more intense as the neuroma enlarges and the temporary changes in the nerve become permanent.
Diagnosis
A GP (general practitioner, primary care physician) or a podiatrist (foot specialist doctor) will ask the patient to describe the pain as well as its intensity, when symptoms started, what types of shoes are worn, as well as some questions about their job, lifestyle and hobbies. The doctor will then examine the foot and try to locate the affected nerve. This may involve attempting to reproduce symptoms by manipulating the foot. In order to get a detailed image of the inside of the food, one of the following scans may be ordered. X-ray, this is a type of high-energy radiation. In low doses they are used to diagnose diseases and condition by making pictures of the inside of the body. In higher doses they are used to treat cancer. This procedure is non-invasive and painless. Ultrasound scan, high frequency sound waves are pointed at a specific part of the body, which in this case is the foot. The ultrasound waves bounce of tissues; their echoes are then converted into a picture, called a sonogram. This allows the doctor to get an inside view of the foot. This procedure is non-invasive and painless. MRI (magnetic resonance imagining) a device that uses a magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed images of the body. Unlike CT scanning or general x-ray studies, no ionizing radiation is involved with an MRI. This procedure is non-invasive and painless. The doctor will have to rule out other conditions which may have similar symptoms, including capsulitis, bursitis, or Freiberg’s disease.
Non Surgical Treatment
Orthotics and corticosteroid injections are widely used conservative treatments for Morton?s neuroma. In addition to traditional orthotic arch supports, a small foam or fabric pad may be positioned under the space between the two affected metatarsals, immediately behind the bone ends. This pad helps to splay the metatarsal bones and create more space for the nerve so as to relieve pressure and irritation. It may however also elicit mild uncomfortable sensations of its own, such as the feeling of having an awkward object under one’s foot. Corticosteroid injections can relieve inflammation in some patients and help to end the symptoms. For some patients, however, the inflammation and pain recur after some weeks or months, and corticosteroids can only be used a limited number of times because they cause progressive degeneration of ligamentous and tendinous tissues.
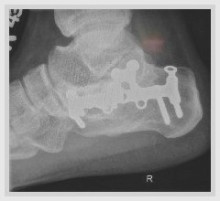
Surgical Treatment
The ultimate success of a Morton?s neuroma treated surgically can be variable. In cases where the underlying problem is only an irritated nerve (a true Morton?s neuroma), then surgery will probably be curative (although it may take a few months for the foot to fully heal). But in many cases, forefoot pain is more complex. There may be an irritated nerve or two causing pain, but the real problem is often excessive loading of the lesser metatarsals. The generic term for this condition is metatarsalgia. When considering surgery, identifying and addressing these problems may lead to a better end result.


 Overview
Overview Symptoms
Symptoms Prevention
Prevention







You must be logged in to post a comment.